Extensive Reading
Author Info
Background
Existing acceleration methods like Speculative Decoding have limitations:
- Rigid Consistency: They require the Small Language Model (SLM) to match the LLM’s tokens exactly. If the SLM phrases a correct reasoning step differently, speculative decoding rejects it, wasting computation.
- Low Agreement: In complex reasoning tasks, token-level agreement between SLMs and LLMs is often low, leading to frequent rollbacks and minimal speed gains.
Insights
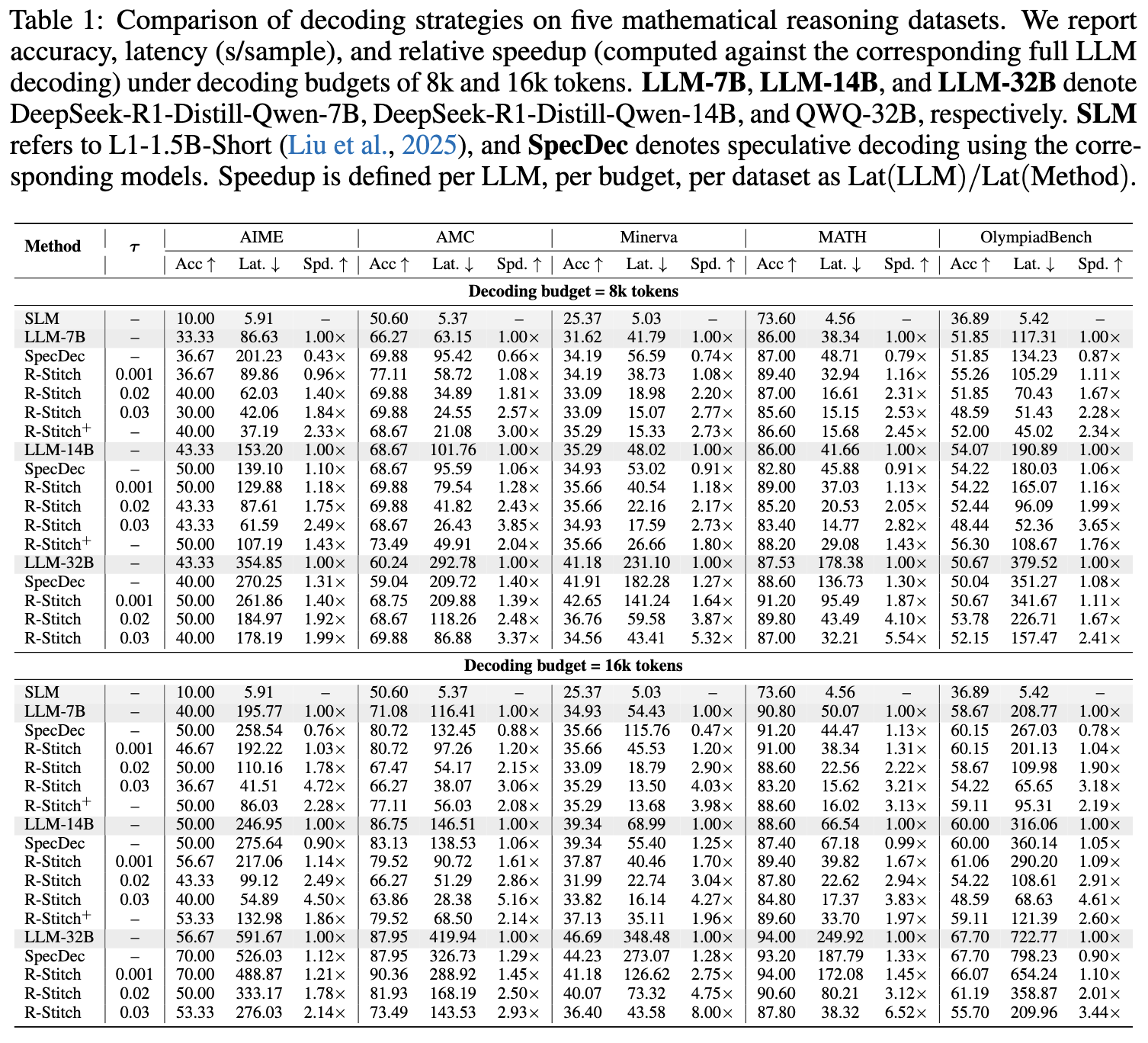
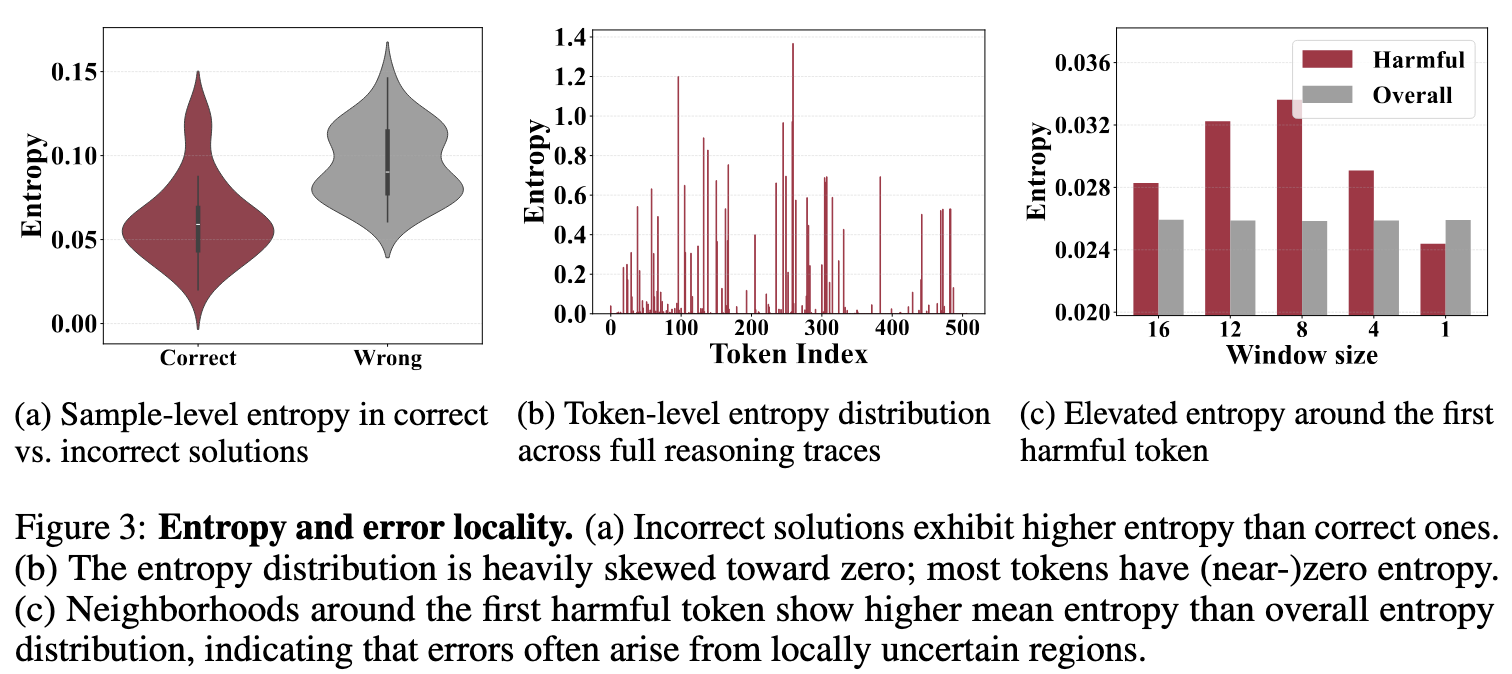
Use entropy as an uncertainty proxy
The paper analyzes entropy patterns on AMC using DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B (LLM) and L1-1.5B-Short (SLM), revealing three key observations:
- Incorrect answers show higher entropy. Reasoning traces leading to wrong answers have significantly higher mean entropy (Figure 3a).
- Most tokens are near-deterministic. Over 89% of SLM tokens have entropy ≤ 0.1, indicating high prediction confidence (Figure 3b).
- High-entropy tokens trigger errors. Harmful tokens are often preceded by locally elevated entropy, making entropy a useful routing signal (Figure 3c).
Approaches
R-Stitch
Entropy-Guided Routing
- The system monitors the normalized entropy ($\mathcal{H}$) of the probability distribution at each decoding step.
- SLM $\rightarrow$ LLM: If the SLM’s uncertainty exceeds a fixed threshold ($\tau$), control is passed to the LLM. The uncertain token is discarded, and the LLM regenerates it.
- LLM $\rightarrow$ SLM: Once the LLM stabilizes and produces a token with low uncertainty ($\le \tau$), control is handed back to the SLM to save computational cost.
Important
R-Stitch switches back to SLM once LLM produce a token with low uncertainty to avoid single-token fluctuation problem.
R-Stich+
To overcome the limitations of a fixed entropy threshold, the authors introduce R-Stitch+, which replaces the heuristic rule with a learned policy.
- Learned Router: A lightweight router (a small MLP head) takes the model’s hidden states as input and outputs a binary decision: continue with the current model or switch.
- Latency-Aware Reward Function:The router is trained using Reinforcement Learning (specifically the DAPO algorithm). The reward function ($R$) explicitly balances accuracy and real-world latency:$$R = r_{acc} + r_{eff}$$
- Accuracy ($r_{acc}$): Binary reward for correct final answers.
- Efficiency ($r_{eff}$): Modeled as $-\lambda \cdot r_{acc} \cdot \hat{L}$, where $\hat{L}$ is the estimated trajectory latency. Crucially, latency is only penalized if the answer is correct, preventing the model from learning to output short, incorrect nonsense just to be fast.
- Latency Estimation:Since measuring wall-clock time during RL training is impractical, the authors use a regression model to estimate latency based on the number of tokens processed (prefill length) and the current KV cache size.
Evaluation
Important
论文观察到 SLM 通常具有更小的输出长度,所以在 Benchmark 中,Latency 汇报的是 Sample 级别的时间开销,这样就能说通为什么 LLM USAGE 不低的情况下,加速比还这么明显了,有一点 Tricky, 但是也合理