AI-Aided
Author Info
Background
- The Bottleneck: LLM inference is slow due to its auto-regressive nature and memory bandwidth constraints.
- Existing Solution (Speculative Decoding): Standard Speculative Decoding (SD) uses a small “draft model” to predict a fixed number of tokens ($K$), which are then verified by the larger “target model”.
- The Limitation: SD relies on a fixed window size ($K$). If $K$ is too large, the draft model generates bad tokens that waste time; if $K$ is too small, it limits potential speedups. Previous methods to adjust $K$ dynamically often required extra training or complex resource management.
Insights
- Use entropy to dynamically decide the window size $K$
- Hierarchical speculative decoding
- Three models: M1,M2,MP
- When the confidence score of M2 is high, draft-verify process only happens between M1 and M2, without MP
Challenges
- Can we dynamically adjust the window size K without requiring any additional training?
- Can we leverage models of different sizes to enhance speed?
Approaches
Self-verify: verify the draft token by itself
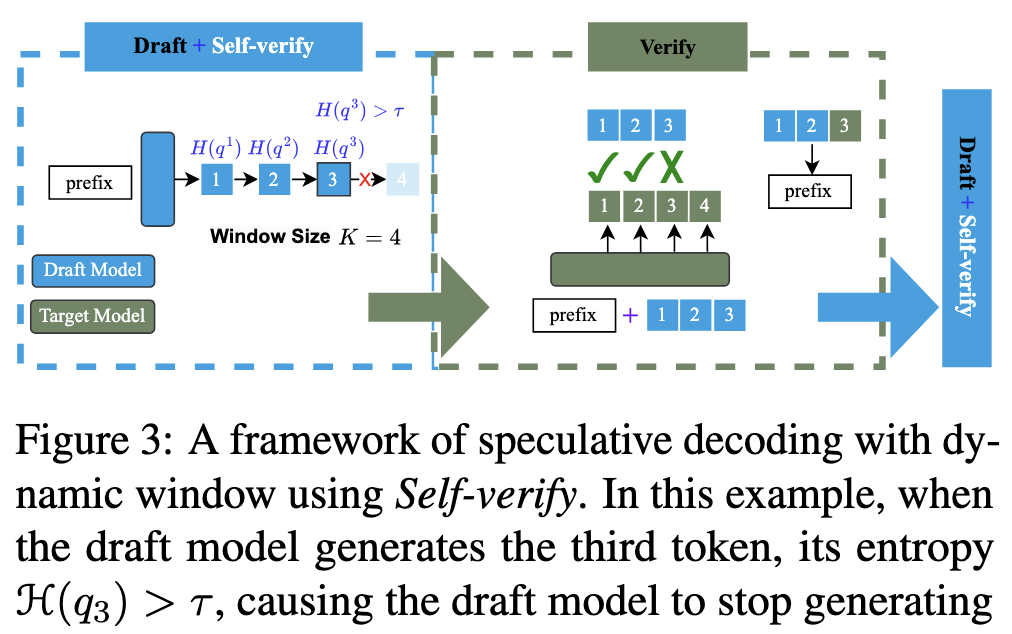
- Entropy-Based Stopping: The model calculates the entropy $\mathcal{H}(q_t)$ of its predicted token distribution at each step.
- Confidence Threshold ($\tau$):
- If the entropy is low ($\le \tau$), the model is confident and continues generating.
- If the entropy is high ($> \tau$), the model is unsure and stops generation immediately to proceed to verification.
- Dynamic Adjustment: The threshold $\tau$ is not fixed; it is dynamically updated based on the average entropy of tokens that were actually rejected by the target model in the current sequence.
根据被拒 token 自动调节 threshold 有点意思
Hierarchical Structure
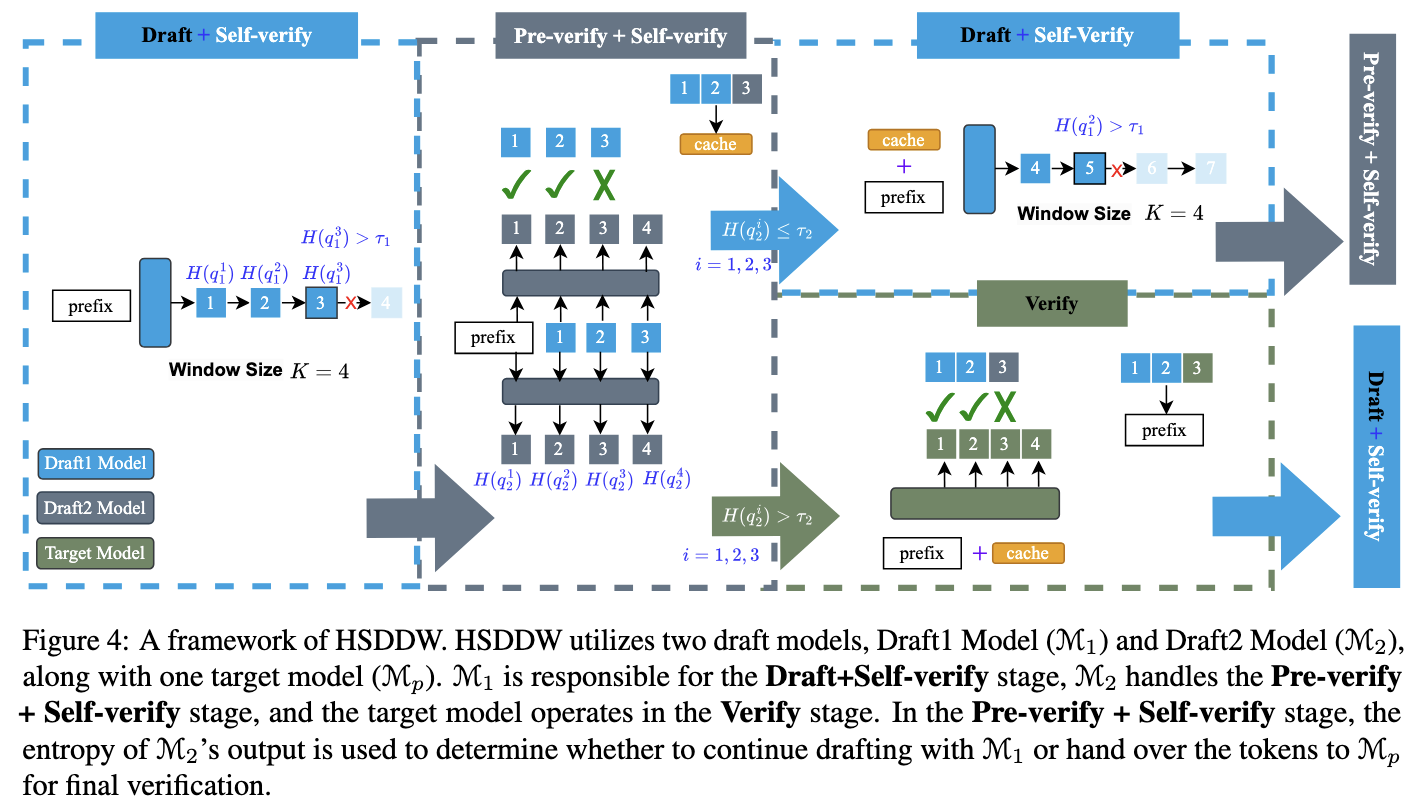
To further maximize speed, the framework uses three models instead of two: a Fast Draft Model ($\mathcal{M}_1$), a Stronger Draft Model ($\mathcal{M}_2$), and the Target Model ($\mathcal{M}_p$).
The process consists of three distinct stages:
- Draft + Self-verify
- The smallest model, $\mathcal{M}_1$, generates initial tokens. It uses the Self-verify mechanism to stop drafting as soon as its confidence drops.
- Pre-verify + Self-verify
- The generated tokens are passed to the medium-sized model, $\mathcal{M}_2$.
- $\mathcal{M}_2$ acts as a “pre-verifier.” It checks the tokens and also performs its own Self-verify check.
- If $\mathcal{M}_2$ is confident ($\mathcal{H} \le \tau_2$), the process can loop back to $\mathcal{M}_1$ to generate more tokens.
- If $\mathcal{M}_2$ loses confidence, the batch is sent to the final stage.
- Verify
- The large target model ($\mathcal{M}_p$) performs the final parallel verification of all tokens generated.
Evaluation
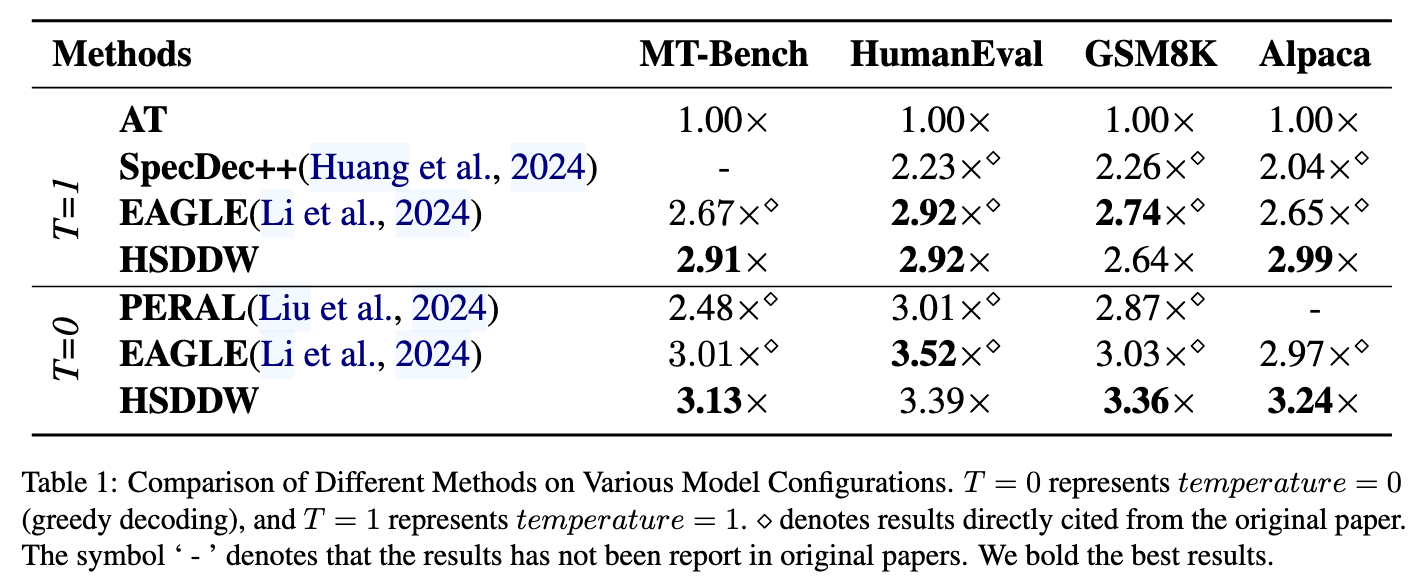
Ablation Study
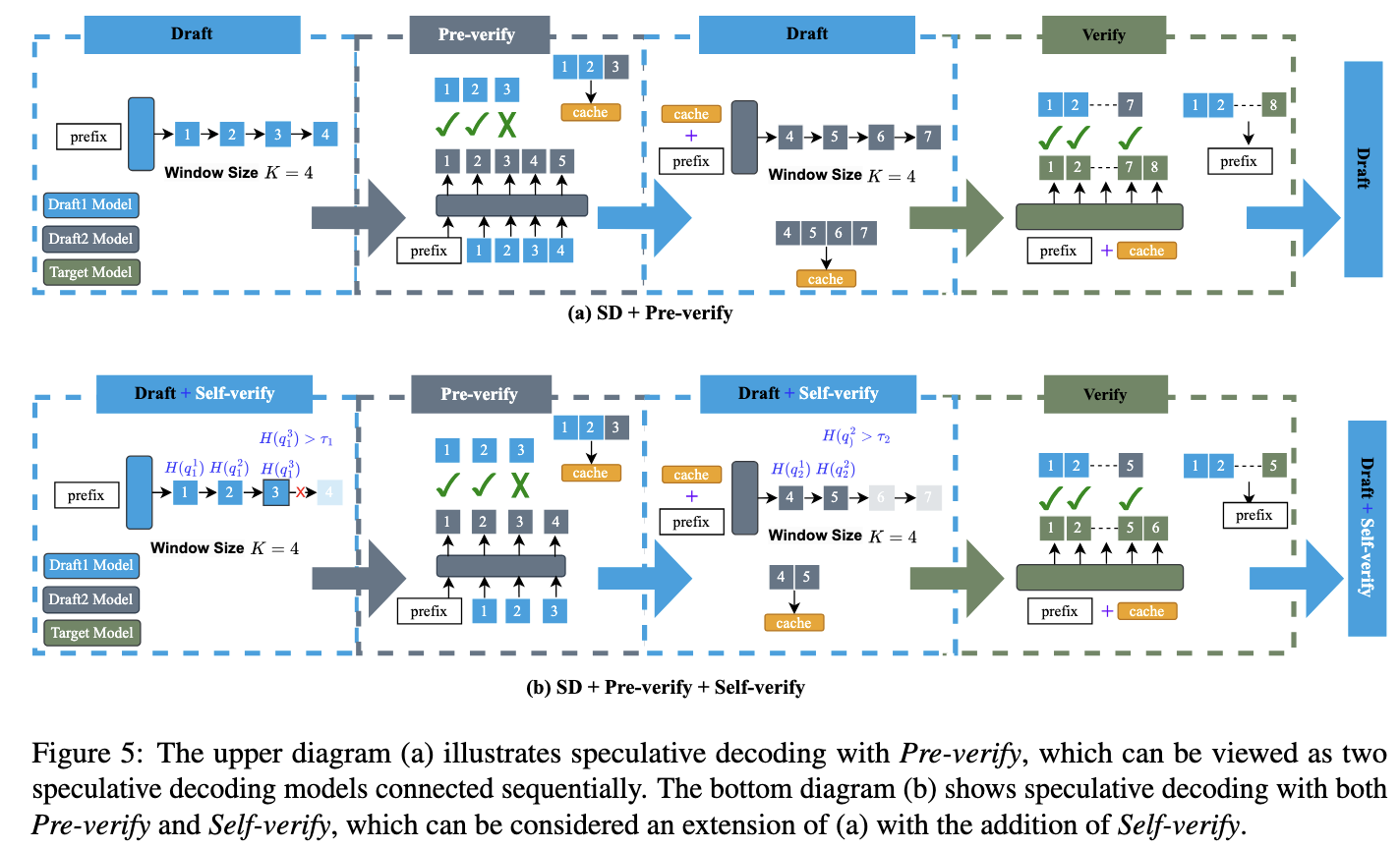
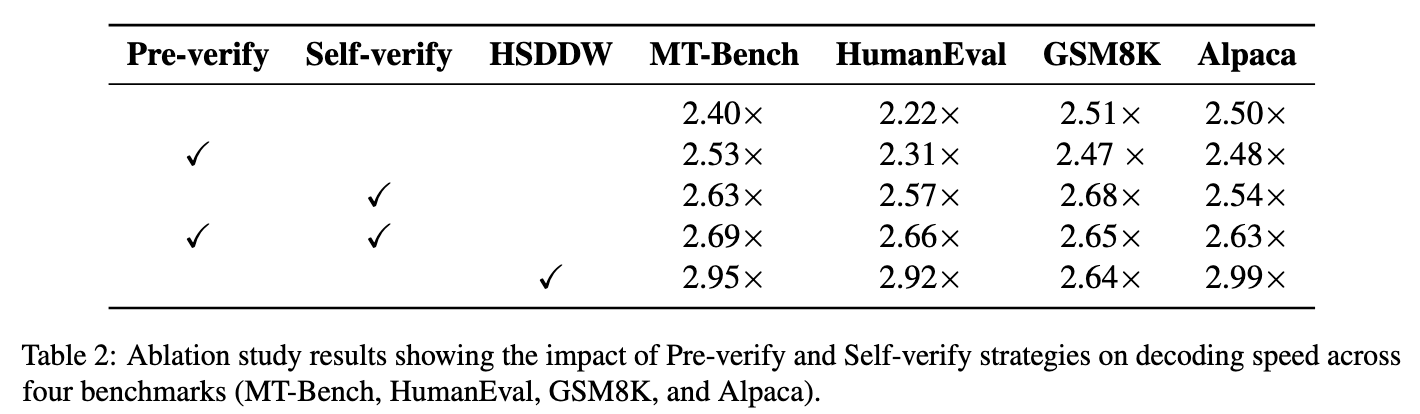
Note
Pre-verify + Self-verify 和 HSDDW 不同的地方就是没有 Loop Back 机制,无论 Draft2 Model 是否通过,都会交给 Target Model
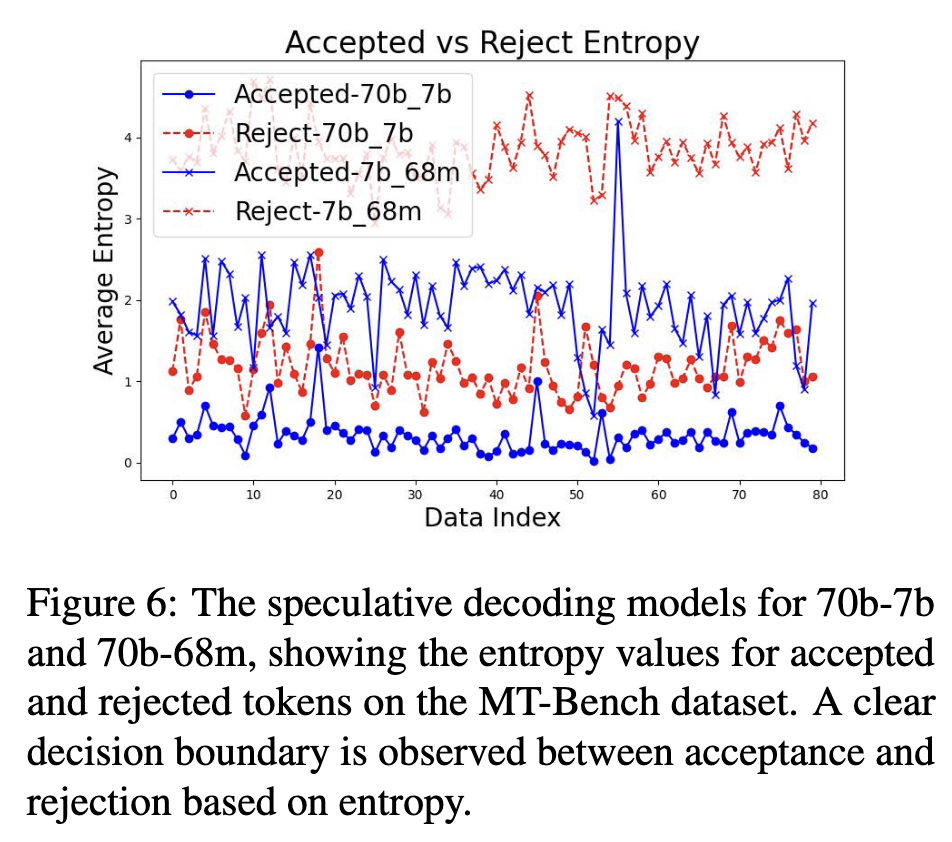
这个图也挺有意思的
Implementation
SD + Self-verify
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def calculate_entropy(logits):
"""
Calculate the Shannon entropy of the probability distribution.
Formula: H(p) = -sum(p * log(p))
"""
probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
log_probs = F.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
entropy = -(probs * log_probs).sum(dim=-1)
return entropy
def sample_greedy(logits):
"""
Extract the token with the highest logit value.
"""
return torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1, keepdim=True)
def speculative_decoding_dynamic_window(
input_ids,
draft_model, # M_q: Small draft model
target_model, # M_p: Large target model
max_new_tokens=100,
gamma=5, # Maximum lookahead window size
initial_tau=0.0
):
"""
Speculative Decoding with Dynamic Window (Self-Verify) using Greedy Sampling.
"""
curr_ids = input_ids.clone()
tau = initial_tau
history_rejected_entropies = []
generated_count = 0
while generated_count < max_new_tokens:
# --- 1. Draft Phase (with Self-Verify) ---
draft_tokens = []
draft_logits_list = []
for k in range(gamma):
with torch.no_grad():
draft_outputs = draft_model(curr_ids)
next_token_logits = draft_outputs.logits[:, -1, :]
# [Self-Verify Mechanism]
current_entropy = calculate_entropy(next_token_logits).item()
# Stop drafting if draft model uncertainty exceeds threshold tau
if len(history_rejected_entropies) > 0 and current_entropy > tau:
break
# Greedy sampling from draft model
next_token = sample_greedy(next_token_logits)
curr_ids = torch.cat([curr_ids, next_token], dim=-1)
draft_tokens.append(next_token)
draft_logits_list.append(next_token_logits)
# Fallback if no tokens were drafted
if len(draft_tokens) == 0:
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = target_model(curr_ids)
next_token = sample_greedy(outputs.logits[:, -1, :])
curr_ids = torch.cat([curr_ids, next_token], dim=-1)
generated_count += 1
continue
# --- 2. Verification Phase ---
with torch.no_grad():
target_outputs = target_model(curr_ids)
# Align target logits: target_outputs.logits[:, i, :] predicts token i+1
start_idx = curr_ids.shape[1] - len(draft_tokens) - 1
target_logits_seq = target_outputs.logits[:, start_idx:-1, :]
accepted_count = 0
rejected = False
for i, draft_token in enumerate(draft_tokens):
target_logits = target_logits_seq[:, i, :]
# Greedy sampling from target model for verification
target_token = sample_greedy(target_logits)
if draft_token.item() == target_token.item():
accepted_count += 1
else:
# --- Rejection & Threshold Update ---
rejected = True
rejected_entropy = calculate_entropy(draft_logits_list[i]).item()
history_rejected_entropies.append(rejected_entropy)
# Update tau: Mean of historical rejected draft entropies
tau = sum(history_rejected_entropies) / len(history_rejected_entropies)
# Rollback to the point of divergence
keep_len = curr_ids.shape[1] - len(draft_tokens) + accepted_count
curr_ids = curr_ids[:, :keep_len]
# Append the correct token from the target model
curr_ids = torch.cat([curr_ids, target_token], dim=-1)
break
# Extra token if all drafts were correct
if not rejected:
last_logits = target_outputs.logits[:, -1, :]
bonus_token = sample_greedy(last_logits)
curr_ids = torch.cat([curr_ids, bonus_token], dim=-1)
accepted_count += 1
generated_count += accepted_count
return curr_ids
HSDDW
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def calculate_entropy(logits):
"""
Calculate entropy H(p) = -sum(p * log(p))
"""
probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
log_probs = F.log_softmax(logits, dim=-1)
entropy = -(probs * log_probs).sum(dim=-1)
return entropy
def algorithm_2_hsddw(
input_ids,
model_m1, # Fast Draft Model (e.g., 68M)
model_m2, # Strong Draft Model / Proxy Verifier (e.g., 7B)
model_mp, # Target Model (e.g., 70B)
max_new_tokens=200,
initial_tau=0.1
):
"""
Algorithm 2: HSDDW - Hierarchical Speculative Decoding with Dynamic Window
"""
curr_ids = input_ids.clone()
# Initialize dynamic thresholds for M1 and M2
tau_q1 = initial_tau # Threshold for M1
tau_q2 = initial_tau # Threshold for M2
# History of rejected entropies for updating thresholds
history_h_q1 = []
history_h_q2 = []
# Initial State
# mode: "Draft" means M1 generates, M2 verifies.
# mode: "Verify" means we send accumulated tokens to Mp.
mode = "Draft"
# 'pending_tokens' stores tokens generated by M1/M2 that haven't been seen by Mp yet.
pending_tokens = []
step = 0
while step < max_new_tokens:
if mode == "Draft":
# --- PHASE 1: DRAFT LOOP (M1 generates, M2 verifies) ---
# 1. M1 generates tokens (Self-verify with tau_q1)
# -------------------------------------------------
new_draft_tokens = []
m1_logits_list = []
# M1 tries to generate a small chunk (e.g., window size 5)
# Stops early if M1 is uncertain (Entropy > tau_q1)
for _ in range(5):
with torch.no_grad():
# Input is current confirmed context + any pending tokens
context = torch.cat([curr_ids, torch.tensor(pending_tokens)], dim=-1)
m1_out = model_m1(context)
next_logits = m1_out.logits[:, -1, :]
# Self-verify: Check M1's confidence
h_m1 = calculate_entropy(next_logits).item()
if len(history_h_q1) > 0 and h_m1 > tau_q1:
break # Stop drafting
token = torch.argmax(next_logits, dim=-1, keepdim=True) # Greedy for demo
new_draft_tokens.append(token)
m1_logits_list.append(next_logits)
# Add to temporary context for next M1 step
pending_tokens.append(token)
if not new_draft_tokens:
# Force one step if M1 generates nothing, to avoid infinite loop
# (Implementation detail usually handled by forcing 1 token)
pass
# 2. M2 Verifies M1 (Pre-verify)
# -------------------------------------------------
# M2 acts as the "Target" for M1 in this phase.
# We verify the *newly* generated tokens from M1 against M2
# Context includes confirmed curr_ids + pending_tokens (before this batch)
# Note: For simplicity, assume we run M2 on the full sequence
full_seq = torch.cat([curr_ids, torch.tensor(pending_tokens)], dim=-1)
with torch.no_grad():
m2_out = model_m2(full_seq)
# Identify the logits corresponding to the new draft tokens
# We only verify the tokens M1 just added
start_idx = full_seq.shape[1] - len(new_draft_tokens) - 1
m2_logits_seq = m2_out.logits[:, start_idx:-1, :]
accepted_count = 0
rejected = False
for i, token in enumerate(new_draft_tokens):
m2_logits = m2_logits_seq[:, i, :]
m1_logits = m1_logits_list[i]
# Verification (Standard SD logic / Rejection Sampling)
target_token = torch.argmax(m2_logits, dim=-1)
if token.item() == target_token.item():
accepted_count += 1
else:
rejected = True
# [Update M1 Threshold]
# M1 was wrong, record its entropy to history
h_rejected = calculate_entropy(m1_logits).item()
history_h_q1.append(h_rejected)
tau_q1 = sum(history_h_q1) / len(history_h_q1)
# Truncate pending_tokens to remove the bad token and subsequent ones
# pending_tokens currently has ALL pending (old + new).
# We need to cut at the rejection point.
valid_len = len(pending_tokens) - len(new_draft_tokens) + accepted_count
pending_tokens = pending_tokens[:valid_len]
# Append M2's correction
pending_tokens.append(target_token)
break
# 3. M2 Self-Verify (Decide whether to loop back or verify)
# -------------------------------------------------
# Check M2's entropy on the LAST token it just verified/corrected
last_m2_logits = m2_out.logits[:, -1, :]
h_m2 = calculate_entropy(last_m2_logits).item()
# LOGIC:
# If M2 accepted everything (or corrected) AND M2 is confident:
# We stay in "Draft" mode. We trust M2 to guide M1 further.
if not rejected and h_m2 <= tau_q2:
mode = "Draft"
# Loop continues... M1 will generate more on top of pending_tokens
else:
# If M2 rejected something OR M2 is uncertain:
# We stop the draft loop. It's time to ask the big boss (Mp).
mode = "Verify"
elif mode == "Verify":
# --- PHASE 2: VERIFY LOOP (Mp verifies everything) ---
# Now we have a list of 'pending_tokens' accumulated from the Draft loop.
# Mp needs to verify them all.
full_seq = torch.cat([curr_ids, torch.tensor(pending_tokens)], dim=-1)
with torch.no_grad():
mp_out = model_mp(full_seq)
# Verify pending_tokens against Mp
start_idx = curr_ids.shape[1] - 1
mp_logits_seq = mp_out.logits[:, start_idx:-1, :]
# Note: We also need M2's logits here for rejection sampling math
# if we were doing strict sampling. For greedy, we compare IDs.
final_accepted_count = 0
for i, token in enumerate(pending_tokens):
mp_logits = mp_logits_seq[:, i, :]
target_token = torch.argmax(mp_logits, dim=-1)
if token.item() == target_token.item():
final_accepted_count += 1
else:
# [Update M2 Threshold]
# Mp rejected a token that M2 had approved/generated.
# We need to know M2's entropy at this position to update tau_q2.
# (Assuming we cached it or recompute it)
# h_m2_rejected = ...
# history_h_q2.append(h_m2_rejected)
# tau_q2 = sum(history_h_q2) / len(history_h_q2)
# Correct with Mp's token
final_accepted_count += 1 # The correction counts as 1 valid step
# Truncate and fix pending_tokens logic would happen here
break
# Commit accepted tokens to curr_ids
# (Simplification: assuming we take the verified prefix + 1 correction)
curr_ids = torch.cat([curr_ids, torch.tensor(pending_tokens[:final_accepted_count])], dim=-1)
step += final_accepted_count
# Reset for next round
pending_tokens = []
mode = "Draft" # Go back to drafting with M1
return curr_ids