Extensive Reading
Author Info
Background
- Existing works only consider a token sequence generated by a single SSM for speculation which cannot align well with an LLM due to the model capacity gap between them.
- The probability of a successful alignment between the LLM and the speculated token sequence decays exponentially with the expected alignment length.
Challenges
- How to generate a token tree in a extremely large search space?
- How to verify the whole token tree in a single verfication pass?
Insights
Simultaneously consider a diversity of speculation candidates (instead of just one as in existing approaches) to maximize speculative performance.
These candidates are organized as a token tree.
Approaches
Token Tree Construction
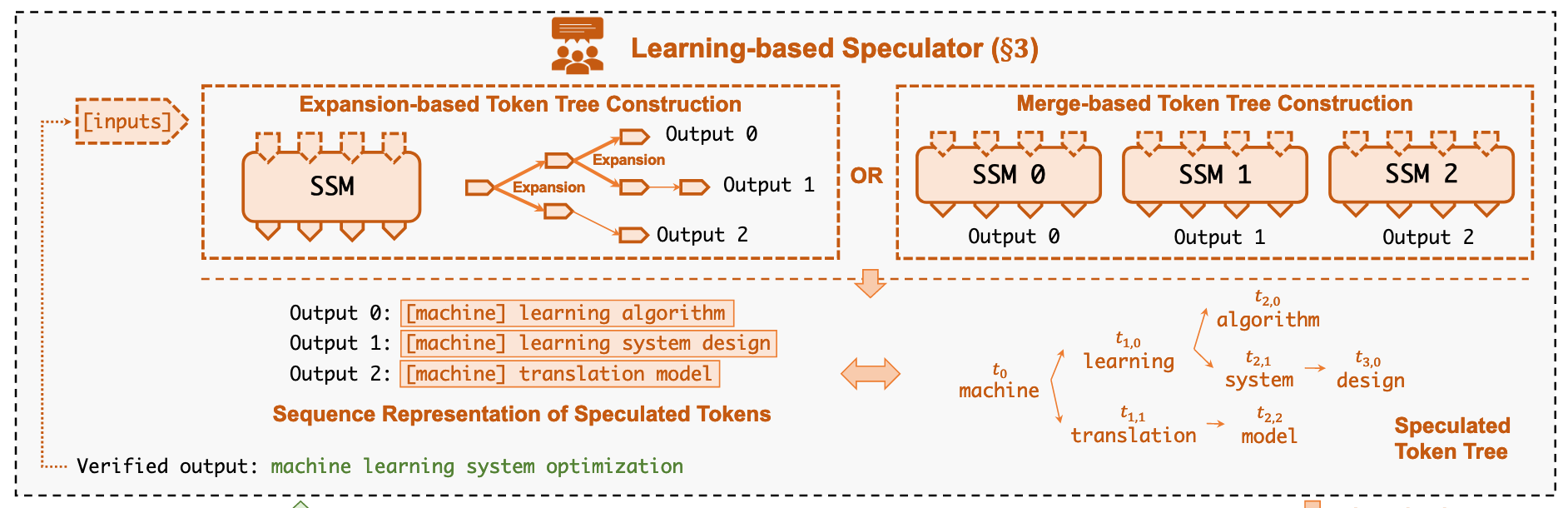
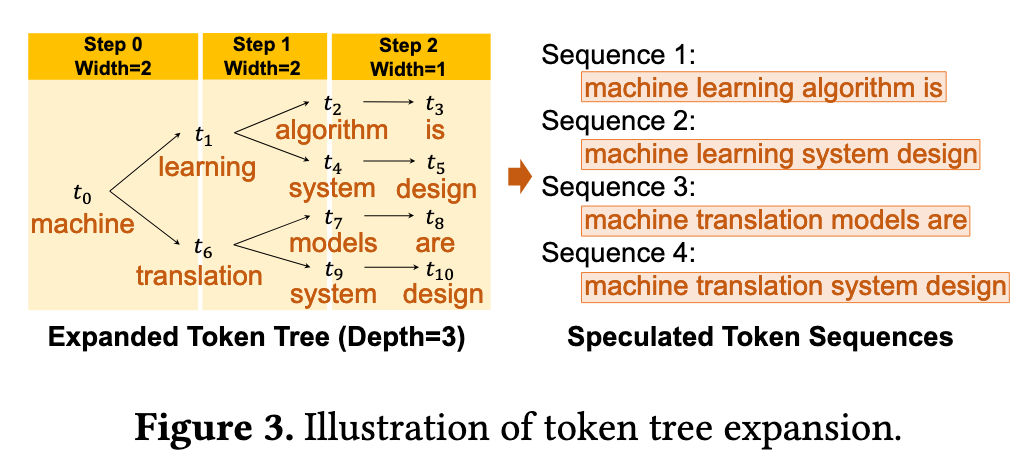
- Expansion-based token tree construction
- Derive multiple tokens from an SSM within a single decoding step.
- 每次 decoding iteration 中选 top-k 就行,也就是在 token tree 中,对于一个父节点,选多个子节点出来。
- SpecInfer employs a static expansion strategy, [[papers/llm/EdgeLLM Fast On-Device LLM Inference With Speculative Decoding|EdgeLLM]] improves this by adopting a dynamic strategy - the branch with higher confidence is intended to be longer and stops speculative generation when the “tree confidence” drops below the threshold.
- Merge-based token tree construction
- 基础思想也很好理解:对于一个确定的输入,每个 SSM 都会并行地输出一个自己预测的序列,然后通过共享前缀的方式组合为 token tree.
- 这里有个问题:如何让不同的 SSM 趋向于生成不同的序列
- SpecInfer 采用了“迭代式专家微调”,利用一个"提示-序列"数据集,对第一个 SSM 进行微调,然后让每个后续的SSM都专注于学习前一个 SSM 预测失败的案例,来达到一种互补的效果。
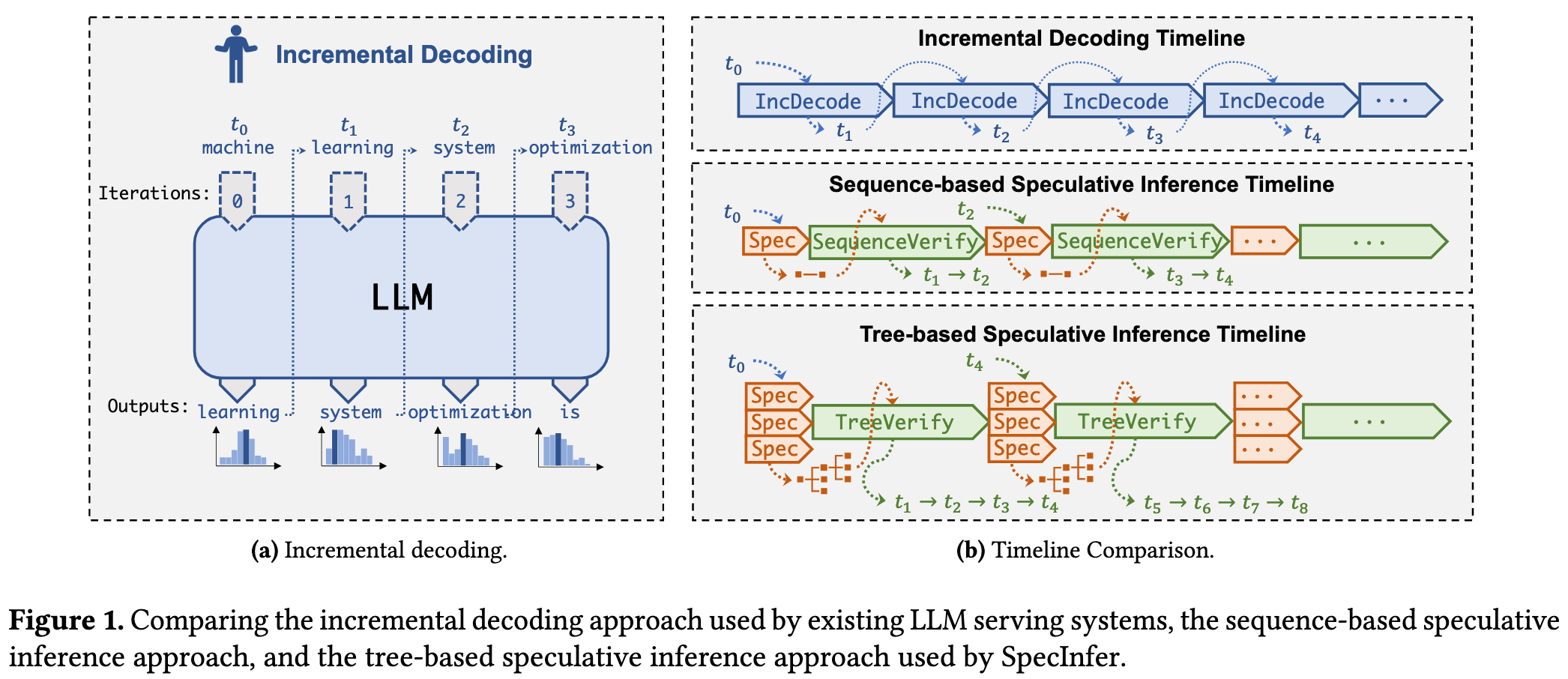
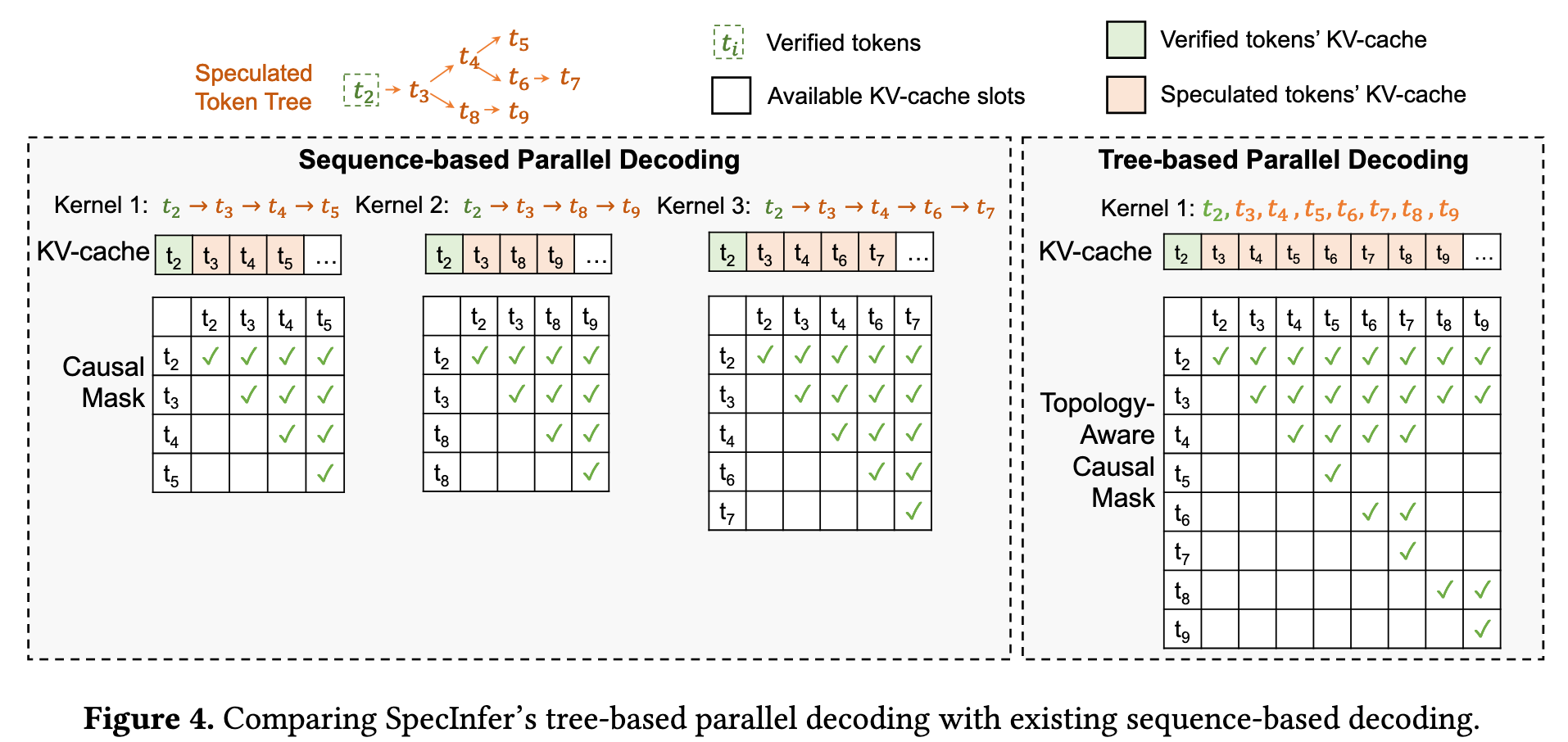
Tree-based Parallel Decoding
Tree attention 部分感觉没什么新意,作者自己硬造了一个概念。
创新点集中在 token tree verification 这部分
把问题抽象出来,就是 kv cache 的存储和注意力计算都是线性的,但输入的 token tree 是树形的,怎么进行统一
- 对于 kv cache
- 让所有路径共用一个缓存,并通过 DFS 的顺序来更新这个缓存
- 对于 attention 计算
- tree 的性质:从根节点出发,有且仅有一条路径可以到达选择的节点,所以 SpecInfer 采用了 Topology-aware Causal Mask,屏蔽掉不应产生影响的Token之间的注意力计算(例如,兄弟节点之间),使得在一次大的矩阵运算中,就能并行且正确地完成树中所有节点的验证。
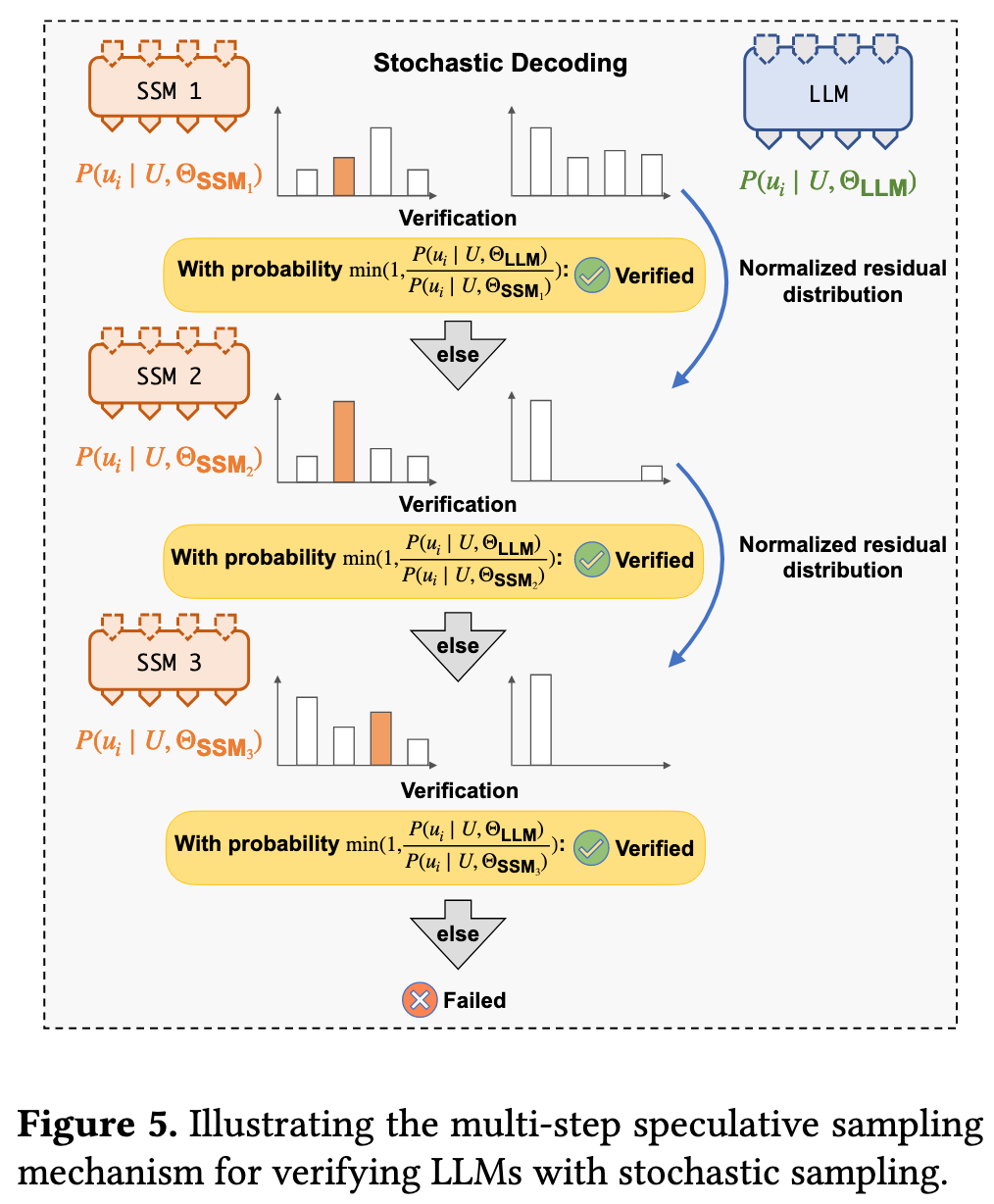
Multi-Step Speculative Sampling
对于需要随机性的“随机解码”(Stochastic Decoding),为了保证生成结果的概率分布与原始LLM完全一致,SpecInfer提出了一种名为MSS的验证算法。
工作原理: 与传统方法先从LLM采样一个Token再看是否在推测中不同,MSS会先检查推测的Token,并以一个精确计算的概率来决定是否接受它。 如果拒绝,它会根据剩余的概率分布重新调整,再对下一个推测的Token进行判断,直到接受一个Token或所有推测都被拒绝为止。
优势: 该算法被证明在数学上与原始LLM的输出分布完全等价 ,同时相比于其他采样验证方法,它拥有更高的推测接受率,能验证更多的Token。