Extensive Reading
Author Info
Background
Existing Speculative Decoding (SD) methods accelerate inference by using a small “draft” model to guess tokens and a large “target” model to verify them. However, these methods usually require training auxiliary models or adding extra parameters, which limits their flexibility (they are not “plug-and-play”).
Insights
LLMs exhibit great potential for self-acceleration through layer sparsity and the task-specific nature of this sparsity.
This paper proposes a method that dynamically determines which layers to skip during inference based on the input, according to these two observations:
- Self-Acceleration via Sparsity: LLMs have inherent redundancy. You can skip many intermediate layers and still get a decent approximation of the next token.
- Figure2 a: 简单地均匀跳过层 + Top-K 预测,也能实现显著的自我加速
- Task-Specific Sparsity: The optimal set of layers to skip varies by task (e.g., reasoning vs. storytelling). A configuration optimized for one task may fail on another.
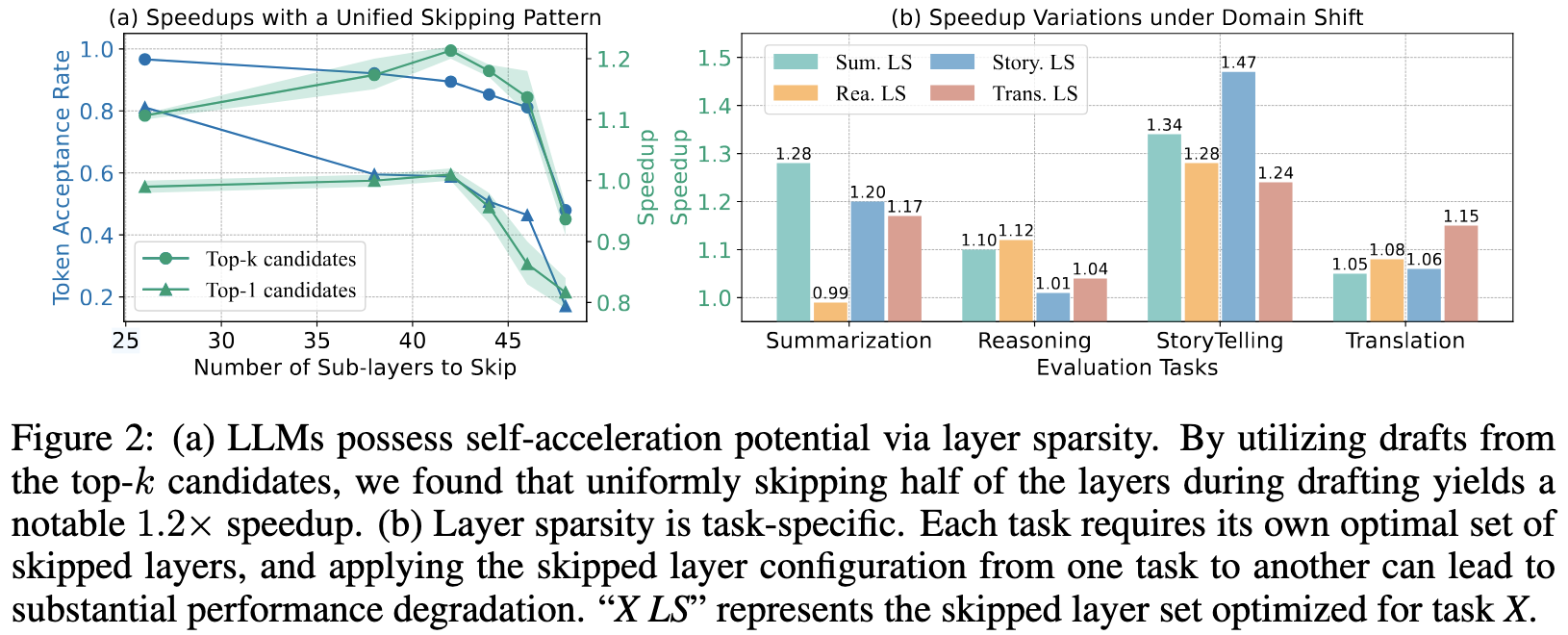
这两个观察对论文的 Motivation 非常有帮助,可以学习一下是怎么组织的:
- Figure 2a 为实时跳层选择提供了坚实的基础,表明可能不需要使用训练数据进行额外的优化
- Figure 2b 强调了静态跳层模式对于各种任务中动态输入数据流的局限性,强调了在推理过程中进行自适应层优化的必要性。
和 Draft & Verify Lossless Large Language Model Acceleration via Self-Speculative Decoding 相比,SSD 使用的是离线静态的贝叶斯优化的方法,SWIFT 使用的是在线动态搜索
所以我们后续重点关注一下是如何实现动态搜索并实现低开销的
Challenges
How to effectively running layer optimization on the fly?
Approaches
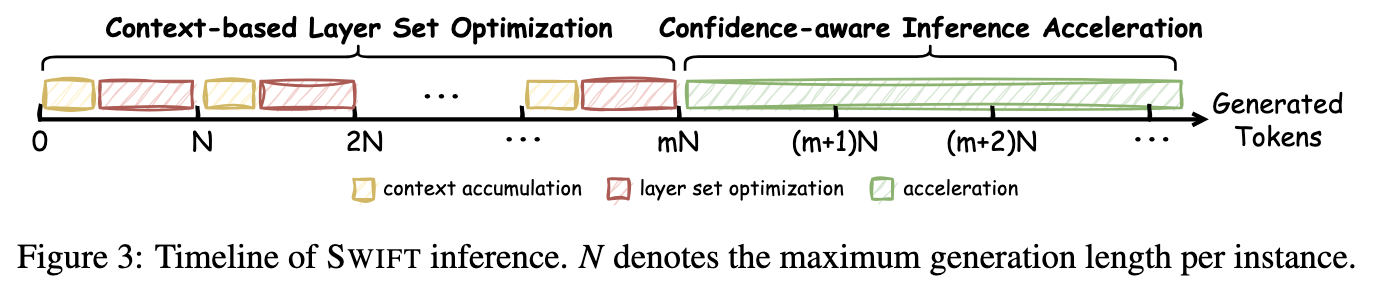
CONTEXT-BASED LAYER SET OPTIMIZATION
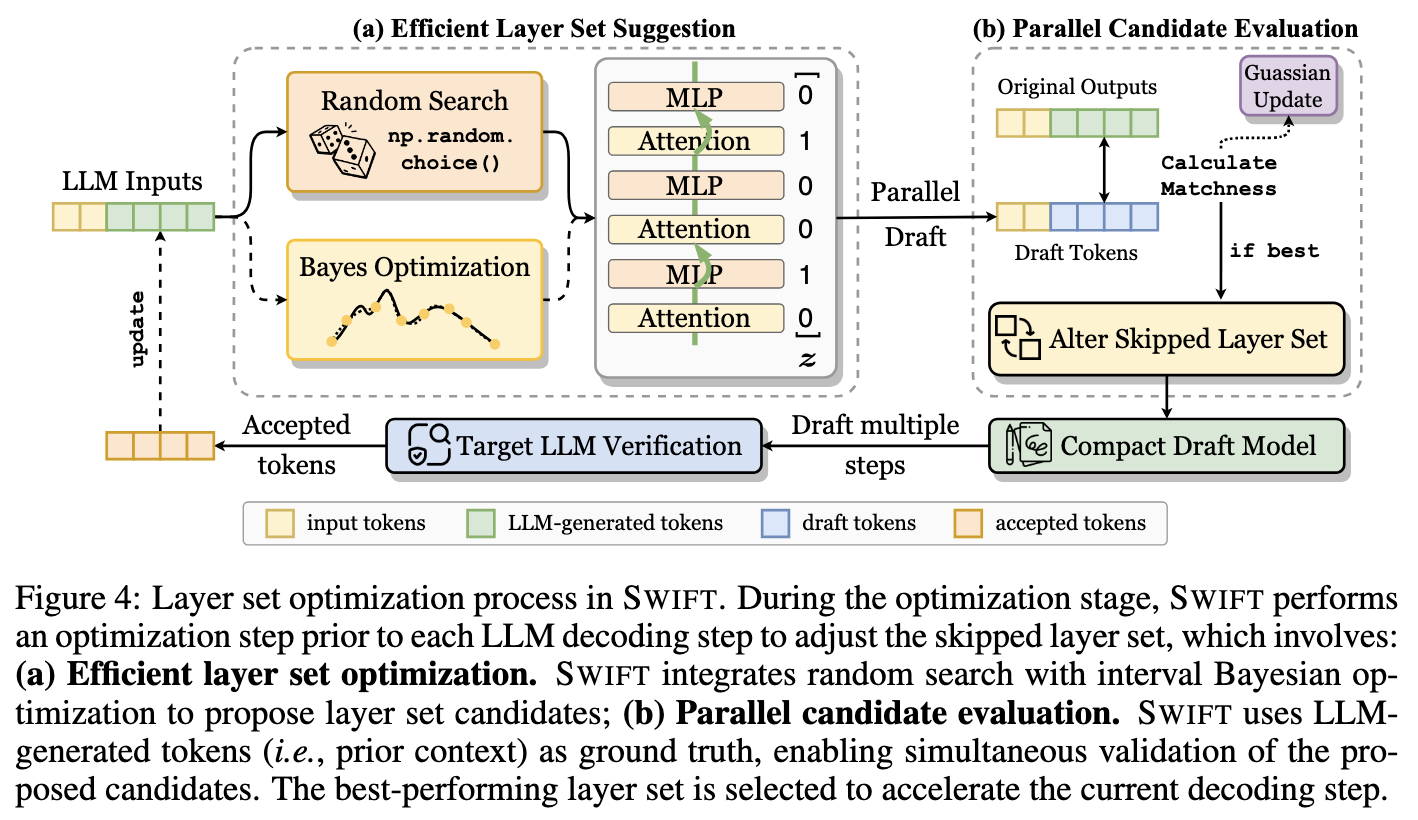
- Suggestion: 系统根据当前的策略(随机搜索或贝叶斯优化)提出一个新的“层跳过配置”(Layer Set Candidate),比如“跳过第 5-10 层”
- Parallel Evaluation: 利用已经生成的 Token(Context)作为“真值”,运行一次 Draft Model(使用刚才提出的层配置)的前向传播。计算该配置在已知 Context 上的 Matchness
- Update: 如果当前候选配置的准确率高于之前的历史最佳配置,则更新“最佳层配置”
这个过程会持续一定步数(例如前 S 步),直到找到足够好的配置,然后进入下一阶段
SWIFT 采用了 Random Search 作为主力,Bayesian Optimization 作为辅助,交替搜索来平衡效率和质量。
Parallel Candidate Evaluation 指的是利用 Transformer 的并行特性,在一次前向传播中同时评估所有历史位置的预测准确性,而不是指同时评估多个候选模型
On-the-fly 含义:
- Phase 1:在生成前几个 Token(或论文设定的前 $S$ 步,如前几十个 Token)时,系统一边生成(通常使用完整模型或当前最佳 Draft),一边进行上述的 Layer Set 搜索。
- Phase 2:一旦搜索结束(达到最大步数或收敛),系统就锁定这个针对当前任务最优的 Layer Set,然后切换到 Self-Speculative Decoding 模式,对后续剩下的所有 Token 进行高速生成。
Confidence-Aware Inference Acceleration
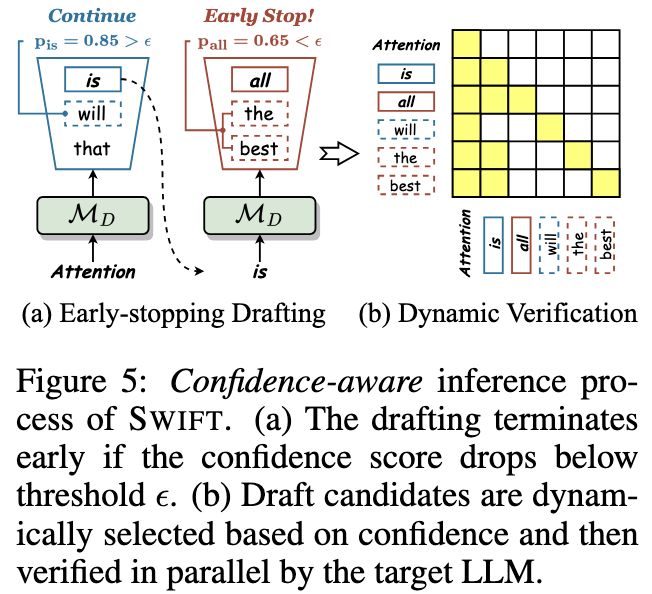
- Early-stopping Drafting
- Drafting process halts if the confidence $p_j$ falls below a specified threshold $\epsilon$
- Dynamic Verification
- 如何利用置信度来构造 Tree Attention 结构,非常的 heuristic
- Each $y'_j$ is dynamically extended with its top-k draft predictions for parallel verification to enhance speculation accuracy
- k is set to 10, 5, 3, and 1 for p in the ranges of (0, 0.5], (0.5, 0.8], (0.8, 0.95], and (0.95, 1]
Evaluation
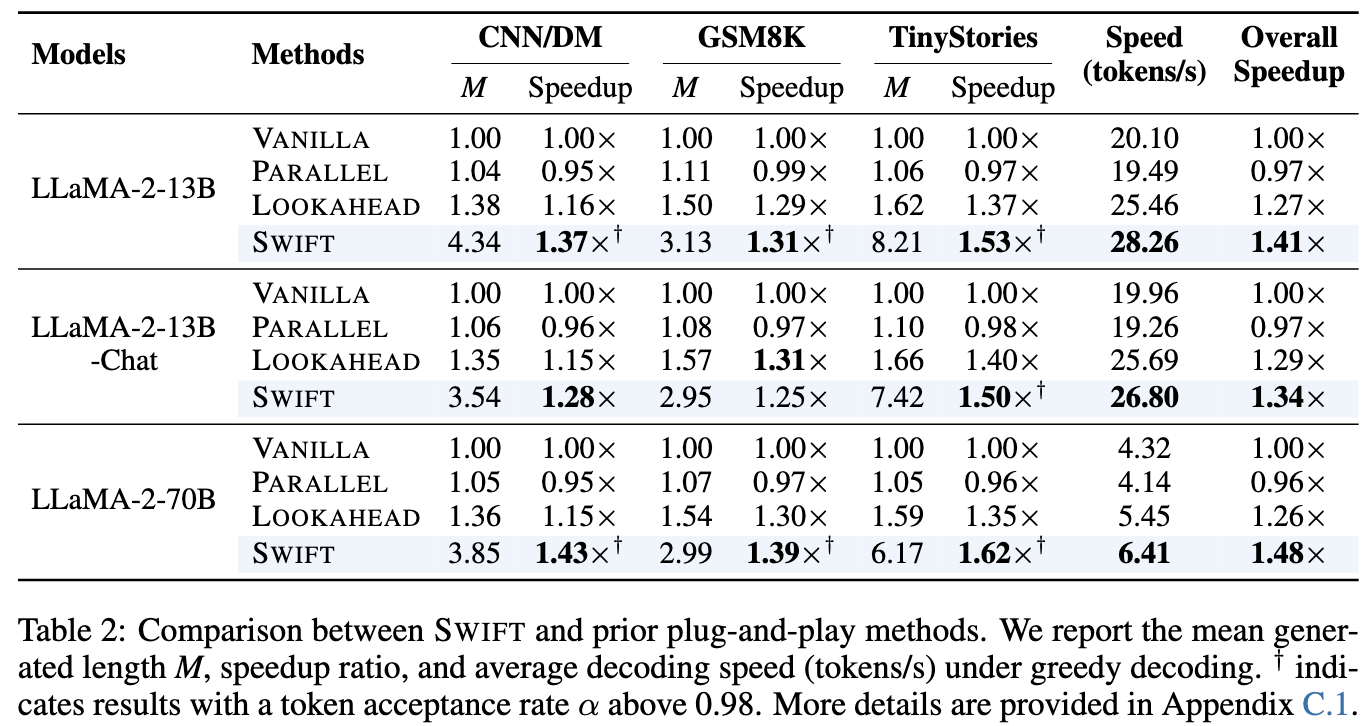
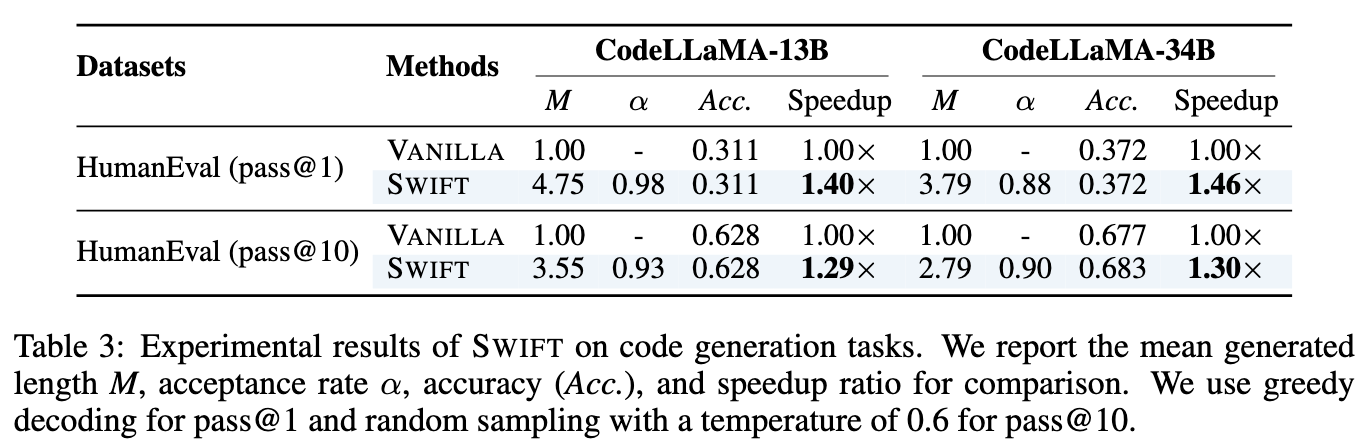
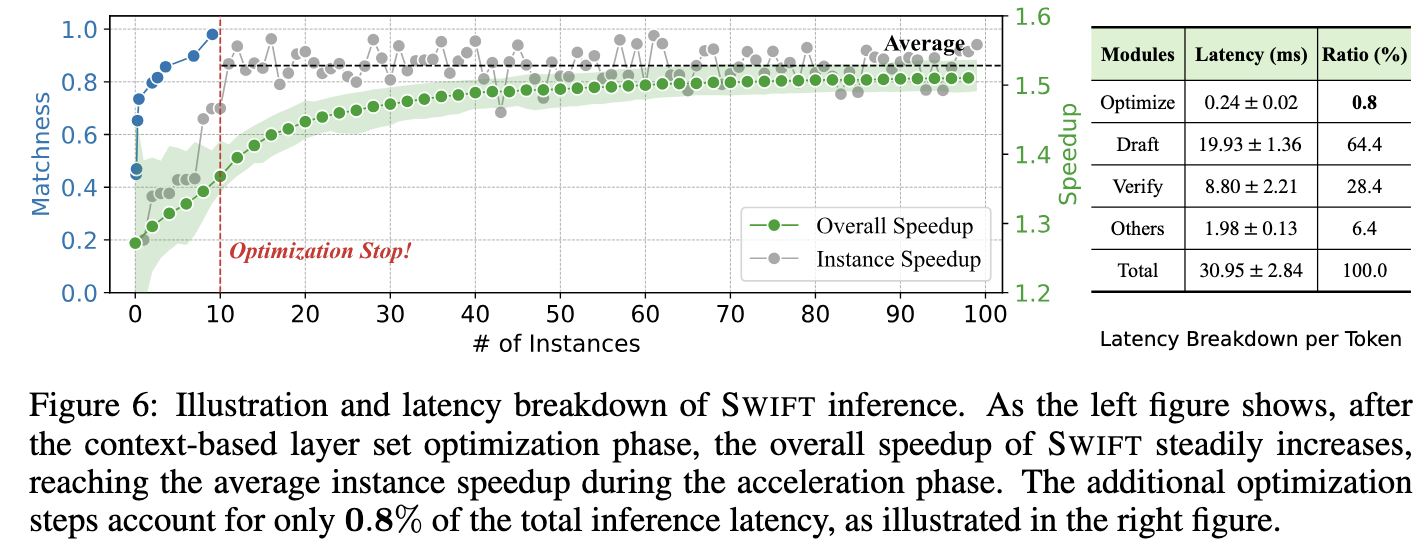
- 横坐标代表处理任务的顺序流。从第 1 个样本开始,一直到第 N 个样本。
- 可以发现在前几个样本中,加速是比较有限的,因为还需要搜索 Layer Optimization
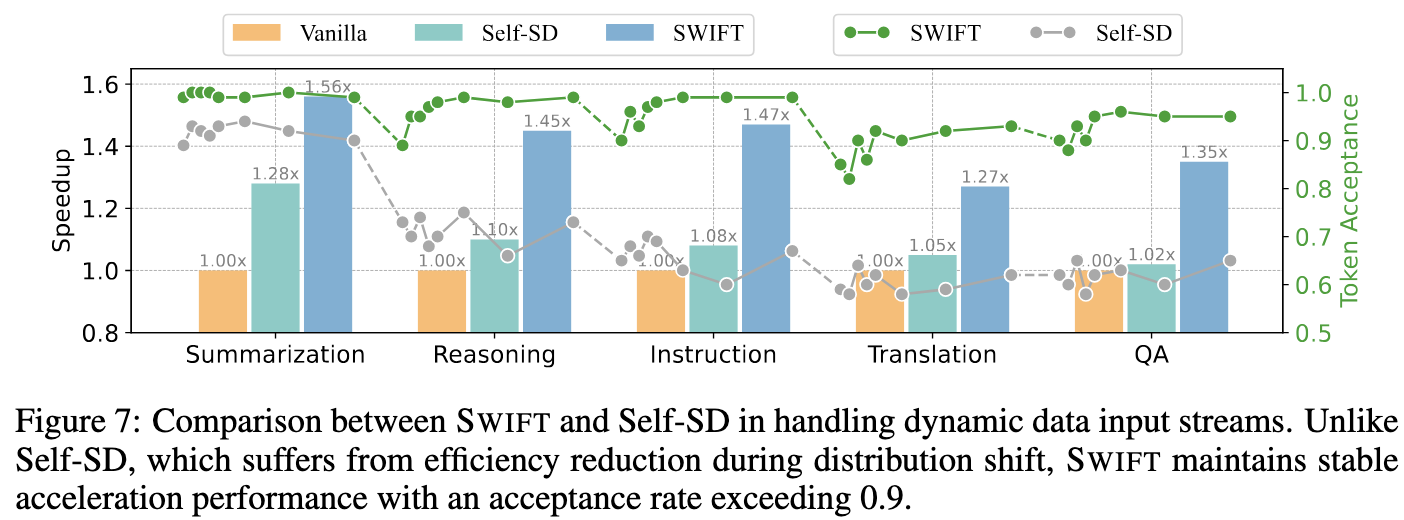
Figure 7 展示了 SWIFT 在处理动态任务时的效果:任务切换时 Token Acceptance 会有一定程度的降低,这会触发新的 Layer Optimization,几个样本之后 Token Acceptance 又会上升
- LLaMA-2 系列跳过比例设置为了 r=0.4
- Yi-34B, DeepSeek-Coder-33B 设置为了 r=0.2
Draft Model 保留了 80% 的 layer, 意思是生成一个 Token 需要 0.8 个单位时间,此时需要配合 SWIFT 超高的 Token Acceptance (0.9+) 才能实现加速
论文中说明:在 代码生成 (Coding) 和 数学推理 (Math) 这种逻辑性极强、很难预测的任务上使用 $r=0.8$
Thoughts
OpenReview
SWIFT: On-the-Fly Self-Speculative Decoding for LLM Inference Acceleration | OpenReview
When Reading
Task-Specific Sparsity 这个思路从方法论上面有启发:
- 如果只考虑 Draft & Verify Lossless Large Language Model Acceleration via Self-Speculative Decoding 这篇工作,静态的 profile 肯定能"进化"为动态的在线搜索
- 并且考虑到了不同任务之间,Sparsity 特性会不会不一致,进而对不同的任务使用不同的配置